SRI vessels, indispensable for offshore wind
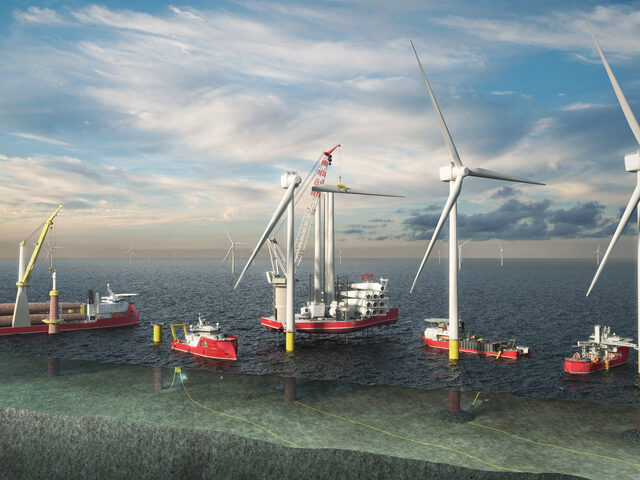
Subsea rock installation (SRI) vessels are widely used in the offshore industry, stabilising and protecting subsea pipelines, cables and other structures at the sea bed. For the offshore wind industry, SRI vessels also lay protective coverings of rock around turbine foundations, to avoid scouring.

Ulstein has a proven track record in developing these highly specialised vessels, the most recent reference being the highly innovative Jones-Act compliant vessel for GLDD, the first of its kind to be built in the U.S. The vessel, an ULSTEIN S211 design, has been developed by Rotterdam based Ulstein Design & Solutions B.V. and will be constructed by Philly Shipyard. The vessel is expected to enter operations by Q4 2024 to serve the U.S. offshore wind market. The contract includes the option for a second vessel.
To reach the low emission and sustainability goals, the vessel design includes EPA Tier 4 engines, plug-in shore power connection for loading in ports and battery packs for peak-shaving. The vessel is also able to run on biofuel to reduce its CO2 footprint and is equipped with active emission control technology to minimise NOx emissions.
In the concept phase, the Ulstein Blended Design method was used to enhance cargo efficiency, boost the GLDD business case, and reduce overall fuel consumption.
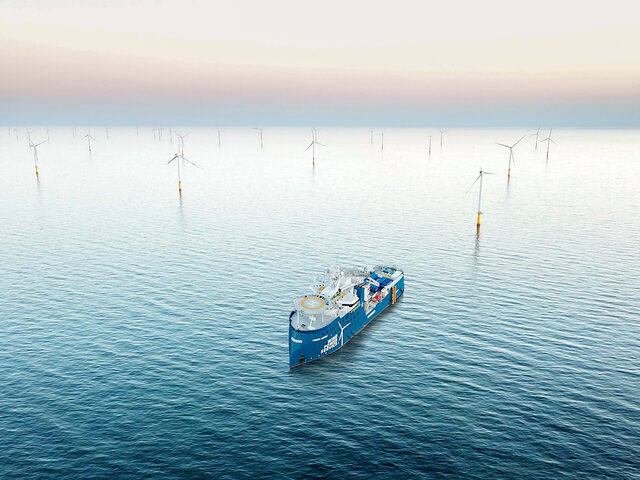
A recent SRI newbuild design, Van Oord's 'Bravenes', is already in operation. This vessel is equipped to perform three different types of rock installation:
- via a flexible fall pipe through the moon pool for deepwater operations
- via a flexible fall pipe over the side for medium water depths
- via a tremie pipe over the side
The latter configuration allows the vessel to install rock very close to offshore structures in shallow water, such as turbine foundations.
Besides its high flexibility in operational rock dumping modes, it is the layout of the vessel that makes a big contribution to the innovative nature of the vessel design. It is the only vessel in its class that features an open top notation, an achievement that Ulstein is especially proud of and rarely seen in offshore vessels.
Together with Van Oord, Ulstein also developed the main Fall Pipe Deployment system (including skidable automatic flexible fall-pipe tower), putting a strong focus on simplicity. By mechanizing the systems as much as possible, higher levels of safety and control and minimising human interaction is achieved when deploying and recovering the fall pipe. The result has been a truly integrated ship design, fully optimised for its core operations: installing rocks subsea.
The rocks are transferred by conveyor belts below the holds to the central hopper, from where the rock enters into the flexible fall pipe. Using a fall-pipe ROV to accurately steer and position the fall-pipe, the rock is placed at the pre-determined location.
Bravenes has been built at Sinopacific Shipbuilding’s Ningbo yard in China and was designed by Ulstein Design & Solutions B.V. in the Netherlands.
Another previous fall-pipe reference is the 'Flintstone' vessel.

Ulstein designed subsea rock installation vessel for GLDD will be America’s first
GLDD orders Jones Act compliant rock installation vessel to serve U.S. offshore wind. The vessel, an ULSTEIN S211 design, has been developed by Rotterdam based Ulstein Design & Solutions B.V. and will be constructed by Philly Shipyard. The contract includes the option for a second vessel.
Carbon conscious solutions
Bravenes
Subsea rock installation vessel, suitable for installation of a wide range of rock sizes through a fallpipe in the moonpool, through a fallpipe over the side or through a tremie pipe over the side. With a DW of 14,000t, a length of 154 m and a beam of 28 m, the vessel can operate in depths of more than 600 metres.
Main dimensions
Feasibility studies
Ulstein carries out multiple studies, one of which is feasibility studies. A feasibility study provides the insight for selecting the best solution towards CAPEX, OPEX and environmental impact. Here's an example of how we can carry out an energy storage feasibility study.
Feasibility studies